Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) has risen in importance in the last three decades in various sectors like aerospace, mechanical, chemical, biotechnology, biomedical etc. CFD is primarily used to design and optimise different equipment and machinery, which are essential in these sectors. CFD involves solving fundamental partial differential governing equations of continuity, momentum, energy, concentration (Navier-Stokes equations) into algebraic equations and solving them simultaneously using numerical techniques. CFD involves three parts: first, geometry creation, second meshing and third, solving of algebraic equations and post-processing. In the first part, the physical equipment is created in two/three-dimension on a geometry creating software. The second part, meshing, involves dividing the geometry created into millions of cubes or tetrahedral elements. The third and final part is done on in-house/commercial codes where equations are solved by providing necessary inputs, and outputs are observed using post-processing software. Commercial codes/software’s like Ansys Fluent/CFX, Comsol, and open-source software’s like OpenFOAM provide these integrated capabilities of performing all the three steps described above.
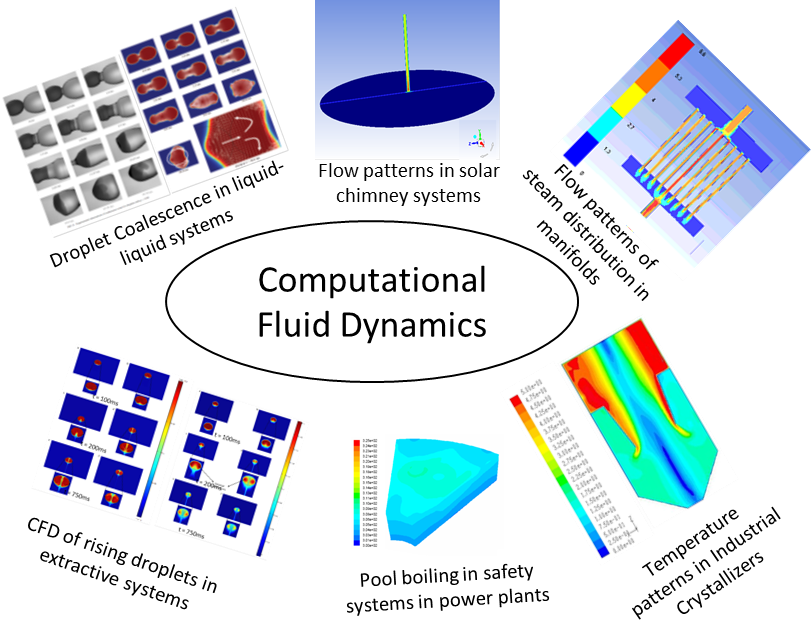
Figure 1 Flow patterns of different systems using commercial CFD software’s
Scale-up of equipment from lab to commercial scale poses a significant challenge due to several transport phenomena. Experimentation of such systems for pilot/bench scale setups involve huge costs, and the internal dynamics depends on analytical models, which are approximate. With the increase in computational power, CFD has proven a good option for modelling scaled versions numerically and then for actual fabrication and testing. Further, CFD helps optimise the equipment so that it can be built with confidence. This decreases the cost of experimentation substantially.
For nearly a decade, I have been involved in CFD simulations for understanding phenomena like boiling, droplet coalescence or design, optimisation and scale-up of process equipments. Figure 1 shows some of the applications studied/optimised using commercial CFD software’s Fluent/Comsol. Some of the salient features of the simulation results are presented below:
- On a smaller scale, CFD has been utilised to understand transport phenomena like mass transfer from drops/bubbles. Figure 1 shows the flow patterns of droplet coalescence where two-dimensional two-phase simulations have been made using Comsol software. Understanding this phenomenon is vital for the design of liquid-liquid extractors in chemical industries
- Further, CFD has been utilised to model large scale industrial equipments like a power plant or process plant. Flow patterns of industrial crystallisers and flow patterns of a scaled-up version of the safety system in a power plant have been presented. These pictures demonstrate the power of CFD to contribute to the scale-up of equipments. Three dimensional CFD simulations have been performed for the cases mentioned
- Flow patterns of steam distribution systems have also been presented. The problem of mal-distribution for full-scale equipment has been addressed by using CFD, and necessary modifications can be made to reduce mal-distribution before actually fabricating equipment for full scale
- Temperature patterns of solar chimney power plants have been presented. Three-dimensional simulations of the solar chimney have been performed in this case.
- Apart from active research, I am interested in teaching core chemical engineering subjects like transport phenomena. I am have developed an elective course on Computational Fluid Dynamics in which the basics of CFD, like discretisation, solving algebraic equations etc., are taught. Hands-on sessions on commercial CFD software’s for the steps described earlier are also taken, and projects related to simple problems are provided to students to understand the actual implementation of CFD in applications.


